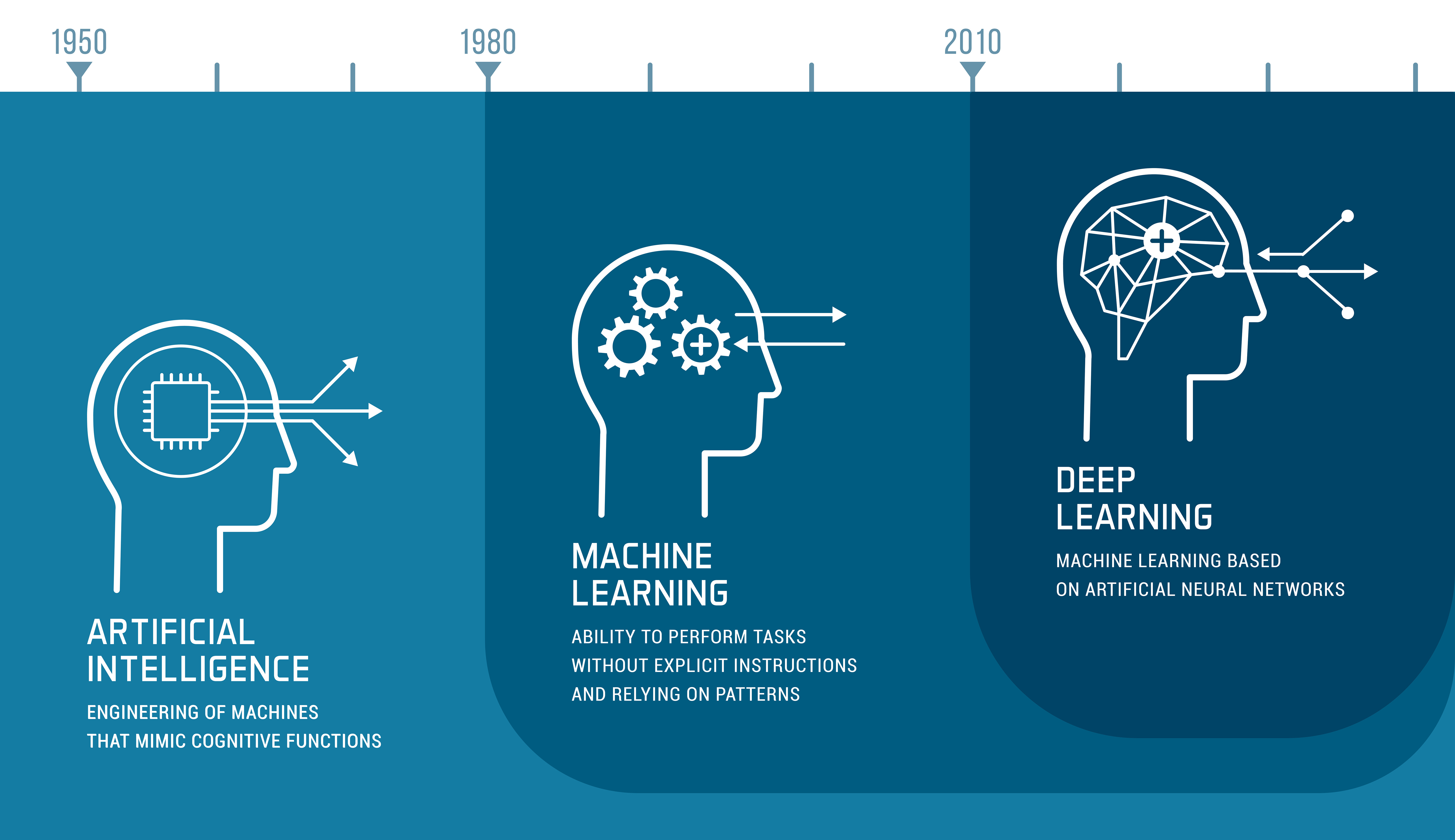
AI: What started as a buzzword, and then became an established term in everyday language, is now a basic requirement for many applications and processes. And this technology is not stopping at the language industry either. Since the launch of ChatGPT we know that translating can now also be completely interactive. Large Language Models, also know as LLMs, in chatbot form are now flooding the market. It feels as though a new model is popping every week, announcing its intention to outdo its competitors in terms of efficiency, quality and reliability. Neural machine translation (NMT) doesn’t seem that old – and yet we are already discussing when this technology will disappear from the market and be replaced by generative AI.
The key question is: I want to translate more efficiently with AI – but how?
AI for targeted optimisation of translation quality
Even though the technology has made significant progress over the last five years, the results of the commonly used and established NMT systems are not always good enough. This can have a variety of causes:
- The desired language combination has not been trained with sufficient material or goes via a pivot language (often English). This can lead to structural problems or errors in meaning.
- The MT system does not recognise specialist or customer-specific terminology.
- The MT system was used for content in which style is extremely important or the translation needs to be targeted towards a specific target group.
Manuals, marketing texts or content with high customer visibility therefore often do not achieve the desired levels of quality through machine translation alone. Language professionals then optimise the machine-generated texts as part of a post-editing process. Machine translations are carefully checked, compared with the source text and corrected if necessary.
As a central translation platform, the CAT tool enables users to work efficiently and offers targeted support for quality assurance thanks to a range of automated features. But where exactly is AI being used here? LLMs such as ChatGPT from OpenAI are perfectly capable of producing translations that, like DeepL or Google Translate, provide a good starting point for further processing, depending on how it is to be used.
However, a significant leap in quality can be achieved by improving the translation requests through the targeted use of prompts and the addition of reference files. To achieve this, however, in addition to a well thought-out prompt engineering design, validated translation resources in the form of translation memory and terminology databases are a fundamental prerequisite.

AI for better translation resources
As with any new technology, a question often arises: What can AI do for me?
However, if you want to integrate AI into your language processes in the long term, you should first ask yourself: What can I do for AI?
Well-maintained translation resources make a significant contribution to improving the results of your AI solution. Take the topic of terminology, for example. If you use a generic system such as DeepL for your translation processes, you will receive translations that do not match your company terminology – unless you integrate a glossary.
Are you only at the stage of establishing your terminology but don’t want to miss out on the benefits of MT? Use language models to extract potential terminology from your monolingual or multilingual documents. You can also use AI to check your translation memory databases, for example to find inconsistent translations or to automate clean-up or correction across large data sets. Use these resources consistently to increase the translation quality of your language model or improve the output of NMT systems.
AI as co-pilot? Reach your destination safely with the new STAR webinar series
As you can see, we are extremely enthusiastic about the topic of AI – and we don’t claim to be reinventing the wheel. However, the technology offers a lot of potential for optimisation if it is used efficiently and sustainably.
Of course, we would like to share our enthusiasm with you and invite you to our webinar series “AI as co-pilot: Forging new paths to smart language processes” starting in March. All the webinars will be held in German only.
How exactly does generative AI actually work? What advantage does it offer for the translation? How can I use language models to create product texts? Can I train my own AI? And what actually happens to my data?
Our Language Technology Consultant Julian Hamm answers these and many other questions and discusses the many different uses of generative AI, including translation, terminology management, content creation and content delivery. You can expect the following content in the first group of topics:
- Was ist generative KI, und wofür kann ich sie einsetzen? (What is generative AI and what can I use it for?)
- Wie kann KI bei der Übersetzung unterstützen? (How can language experts benefit from AI?)
- Wie kann ich KI für die Terminologiearbeit einsetzen? (How can I use AI for terminology work?)
- Welche Vorteile bietet KI für die Content-Erstellung? (What advantages does AI offer for content creation?)
Further information on the events and the registration form can be found here.
We look forward to you joining us!